Two-Phase Heat Transfer
Nucleation superheat
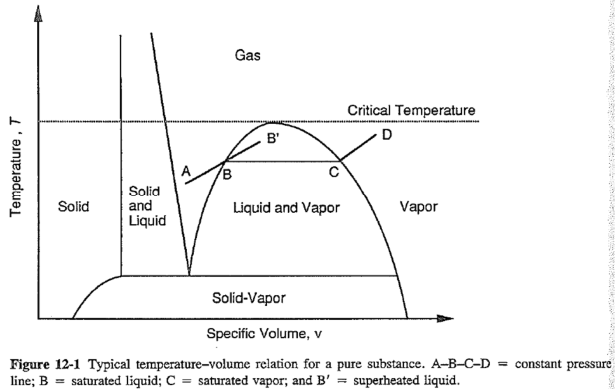
Phase change: liquid -> gas / gas -> liquid
- Homogeneous nucleation 均匀成核 (A-B')
- Heterogeneous nucleation 异相成核 (A-B-C-D)
Specific volume = density
Clausius-Clapeyron relation
Mechanical equilibrium:
: Internal pressure in bubble : Pressure outside the bubble : radius of bubble : coefficient of surface tension 表面张力
Clausius-Clapeyron relation b/w
The Clausius-Clapeyron equation specifies the temperature dependencies of pressure, most importantly, vapor pressure, at a discontinuous phase transition b/w two phase of matter of a single contituent
Superheat (
when
where
Superheat for homogeneous nucleation of water at
Heterogeneous nucleation: dissolved gas & microcavities at surface
Pool boiling
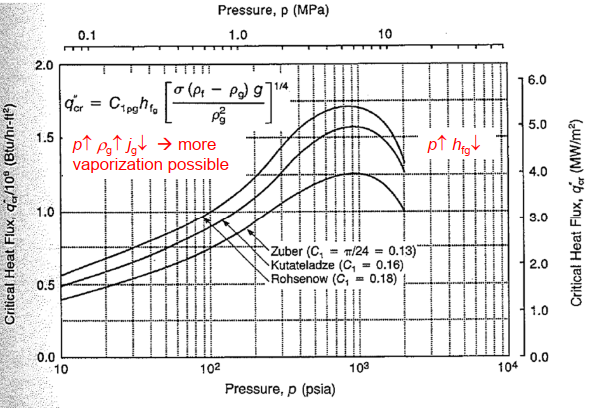
- Boiling curve: Heat-transfer regime of pool boiling
- Critical heat flux: Linked with onset of pool fluidization (suspension of liquid by vapor stream)
Hydrodynamic instability:
- Kelvin- Helmholtz instability: 2 fluid flow counterpart: critical heat flux =...
where
Flow boiling
- Heat transfer regime: Mass flow rate, fluids, geometry, heat flux magnitude and distribution
- Dry-out type CHF: High quality
- DNB (departure from nucleate boiling) type CHF (similar to CHF in pool boiling): Low quality
Enthalpy 焓 [
where:
: heat flux : height w.r.t. the inlet : diameter of pipe : mass flux
comes from
- The area of pipe wall:
- The whole heat:
- The enthalpy increase:
definition: Thermal equilibrium
Two physical systems are in thermal equilibrium if there is no net flow of thermal energy between them when they are connected by a path permeable to heat (From wikipedia)
definition: Thermal equilibrium quality
Thermal equilibrium quality: ratio of the actual enthalpy of a fluid mixture to the enthalpy if it were completely vaporized, assuming the mixture is in thermal equilibrium at the local pressure.
Thermal equilibrium quality at
: Saturated enthalpy : enthalpy of vaporization - When
For boiling curve:
- single-phase flow:
- The corner:
- 2-phase flow:
Subcooled boiling
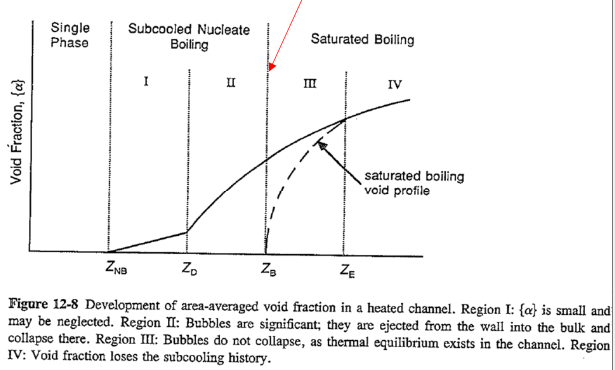
- Region I: Subcooled nucleate boiling (Onset of nucleate boiling (核态沸腾起始点),
: mean or bulk temperature below ) - Region II: Subcooled nucleate boiling (Onset of significant void (显着空洞),
) - Region III: Saturated boiling (
: since liquid does not reach saturation condition due to the bubble presence and non-equilibrium) - Region IV: Saturated boiling (thermal equilibrium condition at
)
- For
, that's Saha-Zuber correlation to determine - For the curve: profile-fit method
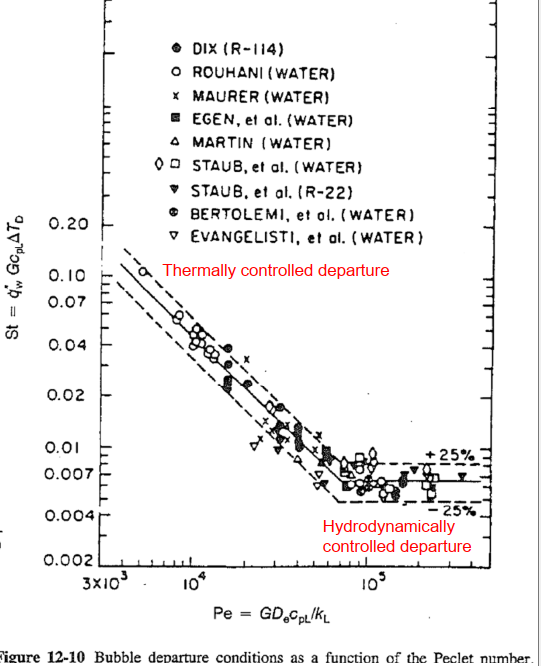
Net vapor generation (Bubble departure)
Net vapor generation: The point at which bubbles can depart from the wall before they suffer condensation (
在流体中,蒸汽的“产生”速度开始大于“凝结”速度,从而出现净增的蒸汽
- Thermally controlled departure: The wall heat flux is balanced by heat removal due to liquid subcooling at
. - Hydrodynamically controlled departure: The bubble detachment is primarily the result of drag (or shear) force overcoming the surface tension force
Saha-Zuber correlation: (empirical)
At first, introduce Peclet number [core]:
where:
: Saturated liquid isobaric heat capacity : Saturated liquid thermal conductivity
no use
For temperature:
and
- 分子:将总质量流量的流体从
显热加热到 所需要的总功率 - 分母:单位长度加热功率
Subcooled flow quality and void fraction
Profile-fit approach: Currently accepted approach for determining the flow quality in subcooled region [core]
The flow quality
at - approaches
asymptotically as increases - When
For quality:
- well-saturated boiling flow:
- Subcooled boiling flow:
Using profile-fit approach to obtain
pump
Mission: prediction of void fraction for heat transfer, etc.
- To predict the void fraction
, the Drift-flux model is used (need )
Drift-flux model:
where
and
is the flow quality
- For HEM,
and 20% overprediction
- Distribution parameter
and drift velocity can be obtained by formulas in the last chapter - To obtain the flow quality
, Profile-fit approach ( ) and OSV model (onset of significant void) are used - To obtain
, Thermal equilibrium quality is used - To obtain
, the Saha-Zuber correlation is used
- To obtain
Saturated Cooling
Heat transfer:
where is the thermal conductivity - Dittus-Boelton equation for
convective heat transfer (Turbulent flow): where
(Saturated boiling flow)
Boling incipience
Fourier's law:
Thus
Quiz3
Water is injected with a velocity of
- Calculate the mixture mass flux (unit in
). In the uniformly heated pipe:
- Calculate the enthalpy at
from the pipe inlet (unit in ).
- Calculate the thermal equilibrium quality located at the
from the pipe inlet. Thermal equilibrium quality is calculated as
- Calculate the Peclet number for the inlet liquid.
- Calculate the temperature for onset of significant void,
, (unit in ). According to Saha-Zuber correlation, when :
Thus
- Calculate the length at which onset of significant void occurs,
, (unit in ).
- Calculate the equilibrium quality at
.
Based on Saha-Zuber correlation, when
- Calculate the quality at
. The quality is calculated based on the profile-fit approach:
where
Thus
(Wrong answer in 7th leads to wrong answer here)
- Calculate the distribution parameter,
, at . Given:
According to the given formula:
Wrong answer
- Calculate the void fraction at
.
The void fraction is calculated by
where
Wrong answer
Thus
Wrong answer
Quiz4
Liquid water with the mass flux
Key information are given below:
- Mass flux:
; - Pressure condition:
; - Inlet temperature condition:
; - Saturation temperature:
; - Liquid enthalpy at inlet:
; - Saturated liquid enthalpy:
; - Saturated gas enthalpy:
; - Latent heat:
; - Saturated liquid density:
; - Saturated liquid dynamic viscosity:
; - Saturated liquid thermal conductivity:
; - Saturated liquid isobaric heat capacity:
; - Saturated gas density:
; - Saturated gas dynamic viscosity:
; - Steam-water surface tension:
; - Steel-water contact angle:
.
Assumptions: (1) Ignore the pressure loss in two-phase mixing section. (2) Air and water fluid compressibility is negligible. (3) Water properties change with temperature is negligible.
- Assume that water properties do not vary significantly in single-phase flow section. Calculate the liquid convective heat transfer coefficient using the Dittus-Boelter equation.
The answer of
Answer:
- What is the temperature difference between the wall temperature and mean bulk liquid temperature (wall super heat [
])?
The answer of
Answer:
- Determine the temperature for the onset of nucleate boiling,
, using Basu et al. (2004) correlation.
where
Answer:
where
Thus
- Calculate the temperature of significant void,
.
The answer of
Answer:
Thus
- Calculate the length for the onset of significant void,
.
The answer of
Answer:
- In another scenario, assume that the heat flux is unknown and the wall temperature is fixed at
. Chen's correlation is used to calculate two-phase heat transfer coefficient and heat flux at . Saturation pressure at is . Calculate the nucleate boiling heat transfer coefficient in Chen's correlation .
where
The answer of
Answer:
- Calculate the convective boiling heat transfer coefficient in Chen's correlation
. Flow conditions are the same as in Question 6.
The answer of
Answer:
- Calculate the total boiling heat transfer coefficient in Chen's correlation
.
The answer of
Answer:
- Calculate the saturation boiling heat flux using Chen's correlation and temperature given in Question 6.
The answer of
Answer:
- Assume that the liquid velocity is zero (pool conditions), calculate the critical heat flux using Zuber's correlation:
where the vapor velocity leading to the onset of fluidization
The answer of
Answer: